Microsoft is trialling a new update to Windows 11’s File Explorer that promises faster searches and lower memory usage, addressing long-standing complaints about resource consumption.
The change is currently being tested in Windows 11 Build 26220.7523 and newer versions available to Windows Insider participants.
According to Microsoft, the update eliminates duplicate file indexing operations during searches, reducing unnecessary system workload.
In a statement, the company explained: “Made some improvements to File Explorer search performance by eliminating duplicate file indexing operations, which should result in faster searches and reduced system resource usage during file operations.”
File Explorer’s search relies on the Windows Search Indexer, which catalogues files for quicker retrieval. Previously, duplicate indexing meant the system could scan the same files or folders multiple times, leading to higher CPU and RAM usage.
By skipping these repeats, Microsoft expects less disk activity, fewer background tasks, and smoother performance during file operations.
This update follows earlier efforts to address File Explorer’s heavy resource demands, including preloading improvements introduced in prior builds. The company is also refining the context menu to reduce clutter.
Options such as “Compress to,” “Copy as path,” “Rotate right,” “Rotate left,” and “Set as desktop background” are being moved into a secondary submenu labelled “Manage file” or “Other actions,” depending on system configuration.
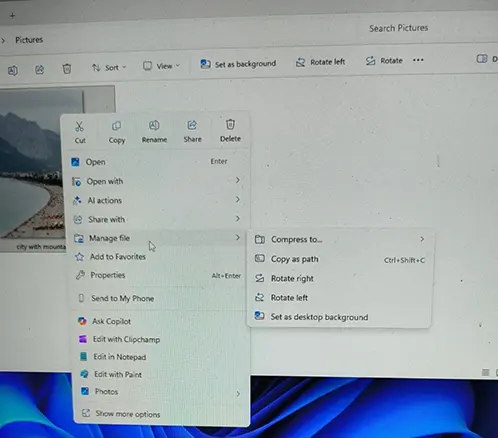
Early testers from Windows Latest reported that the streamlined menu makes navigation more intuitive, while the performance tweaks noticeably reduce lag during searches.
The improvements are still in the testing phase, but Microsoft is expected to roll them out more widely by late January or February.
Analysts suggest the changes could significantly improve everyday usability, particularly for users handling large volumes of images or documents.
For Microsoft, the update reflects its ongoing push to optimise Windows 11’s performance and modernise core features.
With File Explorer remaining one of the most-used applications on the operating system, even small efficiency gains could have a major impact on user satisfaction.
Sources: Windows Blog, Wccftech, Windows Latest